Staying Compliant: Navigating Regulatory Changes in CQV Part 1
by Dhika Prameswari and Rida Hadirah Ramli
In today’s rapidly evolving regulatory landscape, ensuring compliance in Commissioning, Qualification, and Validation (CQV) is increasingly complex and critical for pharmaceutical companies. Keeping pace with regulatory changes is to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of pharmaceutical products. As global standards shift and new guidelines emerge from authorities such as the FDA, EMA, and WHO, companies must continuously adapt their CQV processes to meet these evolving requirements. This article provides an overview of the regulatory changes affecting CQV, exploring how these shifts impact compliance requirements across the industry.
In the second part of this series, we will delve deeper into the practical strategies companies can adopt to stay compliant, including best practices for maintaining compliance and the role of technology in ensuring regulatory adherence. By staying informed and proactive, companies can navigate these changes and uphold both operational efficiency and product quality.
The Evolving Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory environment for CQV is rapidly evolving in response to technological advancements, shifting industry practices, and the rising complexity of pharmaceutical processes. Innovations such as IoT, automation, and advanced data analytics are transforming CQV, enabling faster and more accurate validation processes. However, these advancements bring new regulatory expectations, particularly in data integrity, cybersecurity, and the use of electronic records, where compliance with standards like FDA’s 21 CFR Part 11 is crucial.
One of the most significant changes involves the shift towards real-time monitoring systems, digital signatures, and cloud-based data storage. These technologies improve efficiency in CQV practices, but also demand stricter adherence to regulations, especially in terms of data accuracy and traceability. Companies must ensure their electronic records are secure and compliant with these new standards.
Additionally, industry practices are shifting towards more flexible, adaptive manufacturing models such as continuous manufacturing, which requires an equally adaptive approach to CQV. Furthermore, the increasing complexity of pharmaceutical products adds layers of difficulty in maintaining compliance. This complexity necessitates a robust CQV strategy that can account for intricate production methods and ensure consistent product quality across highly specialized processes. Organizations must stay informed and continuously adapt their CQV frameworks to keep pace with regulatory shifts, ensuring processes meet evolving compliance requirements.
Key Regulatory Bodies and Guidelines
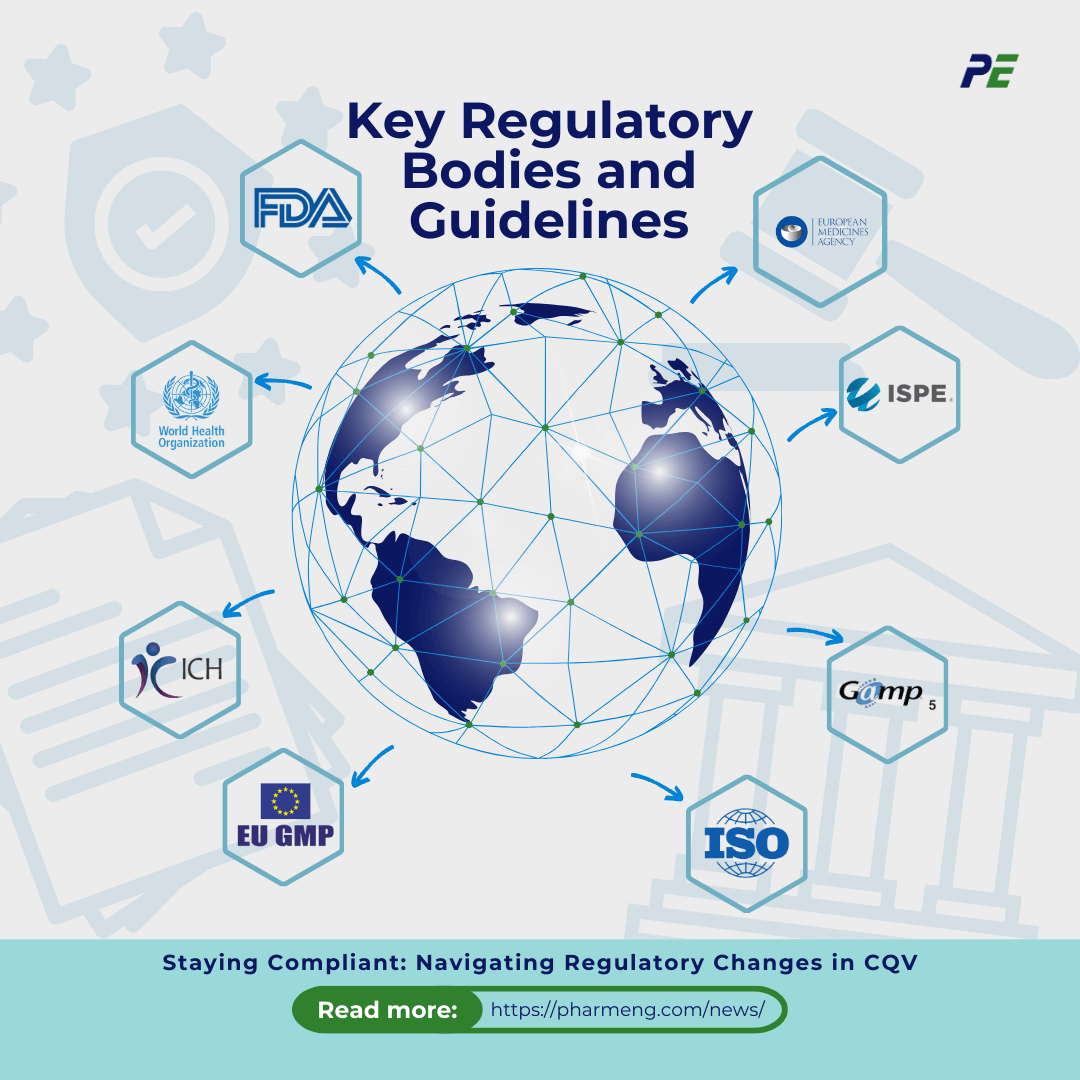
Several major regulatory bodies and guidelines govern CQV practices, shaping how pharmaceutical companies approach the validation of their processes, systems, and products. These bodies set frameworks ensuring product safety, quality, and consistency while adhering to regional and global standards.
1. FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration)
- Key Guidelines:
- 21 CFR Part 11: This regulation establishes requirements for electronic records and signatures, ensuring data integrity, traceability, and security in CQV processes. It governs how electronic systems are used to maintain accurate records and defines standards for electronic audits.
- Significance: FDA regulations influence global validation practices, especially for companies exporting to the U.S. Compliance with FDA guidelines ensures that products meet stringent safety and efficacy standards.
2. EMA (European Medicines Agency)
- Key Guidelines:
- EU Annex 15 (Qualification and Validation): This is part of the EU GMP guidelines and provides a framework for the qualification of systems and equipment and validation of manufacturing processes.
- EudraLex Volume 4: This collection of GMP guidelines applies to the manufacturing, importation, and distribution of medicinal products in the European Union.
- Significance: EMA guidelines influence validation processes across the European market, setting standards for the qualification of facilities, equipment, and computerized systems. Compliance is essential for companies exporting to or operating in Europe.
3. ICH (International Council for Harmonisation)
- Key Guidelines:
- ICH Q8 (Pharmaceutical Development), Q9 (Quality Risk Management), and Q10 (Pharmaceutical Quality System): These guidelines provide a harmonized framework for pharmaceutical quality, focusing on the lifecycle of product development, risk management, and the establishment of quality systems.
- Significance: The ICH guidelines are used globally to harmonize quality standards across different regulatory environments, fostering consistency in CQV practices between regions such as the U.S., Europe, Japan, and beyond.
4. GAMP (Good Automated Manufacturing Practice)
- Key Guidelines:
- GAMP 5: This is an industry-led guide focusing on the validation of automated systems in pharmaceutical manufacturing. It provides a risk-based approach to computerized system validation, promoting efficiency while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Significance: GAMP 5 helps pharmaceutical companies comply with global regulatory requirements for computerized systems, such as those from the FDA and EMA. It ensures that automation technologies, widely used in CQV, are validated and controlled effectively.
5. WHO (World Health Organization)
- Key Guidelines:
- WHO GMP Guidelines: These global standards cover various aspects of good manufacturing practices, including validation, qualification, and process control.
- Significance: WHO guidelines are crucial for global public health and are especially important for countries without their stringent pharmaceutical regulations as they provide a baseline for GMP compliance and validation.
6. ISO (International Organization for Standardization)
- Key Guidelines:
-
- ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems): This is a widely recognized international standard for quality management systems, including processes involved in CQV.
- ISO 13485 (Medical Devices Quality Management): Though primarily for medical devices, this standard sets guidelines for maintaining consistent quality in processes related to product validation.
- Significance: ISO standards are used globally, influencing CQV processes in a wide range of industries, including pharmaceuticals. They emphasize continuous improvement, risk management, and process control.
Impact of Regulatory Updates on CQV
Recent and ongoing regulatory updates have a significant impact on CQV processes in the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries. These changes are driven by the need for greater assurance of product safety, efficacy, and quality in an increasingly complex technological environment. Below are key areas where regulatory changes are having a major impact:
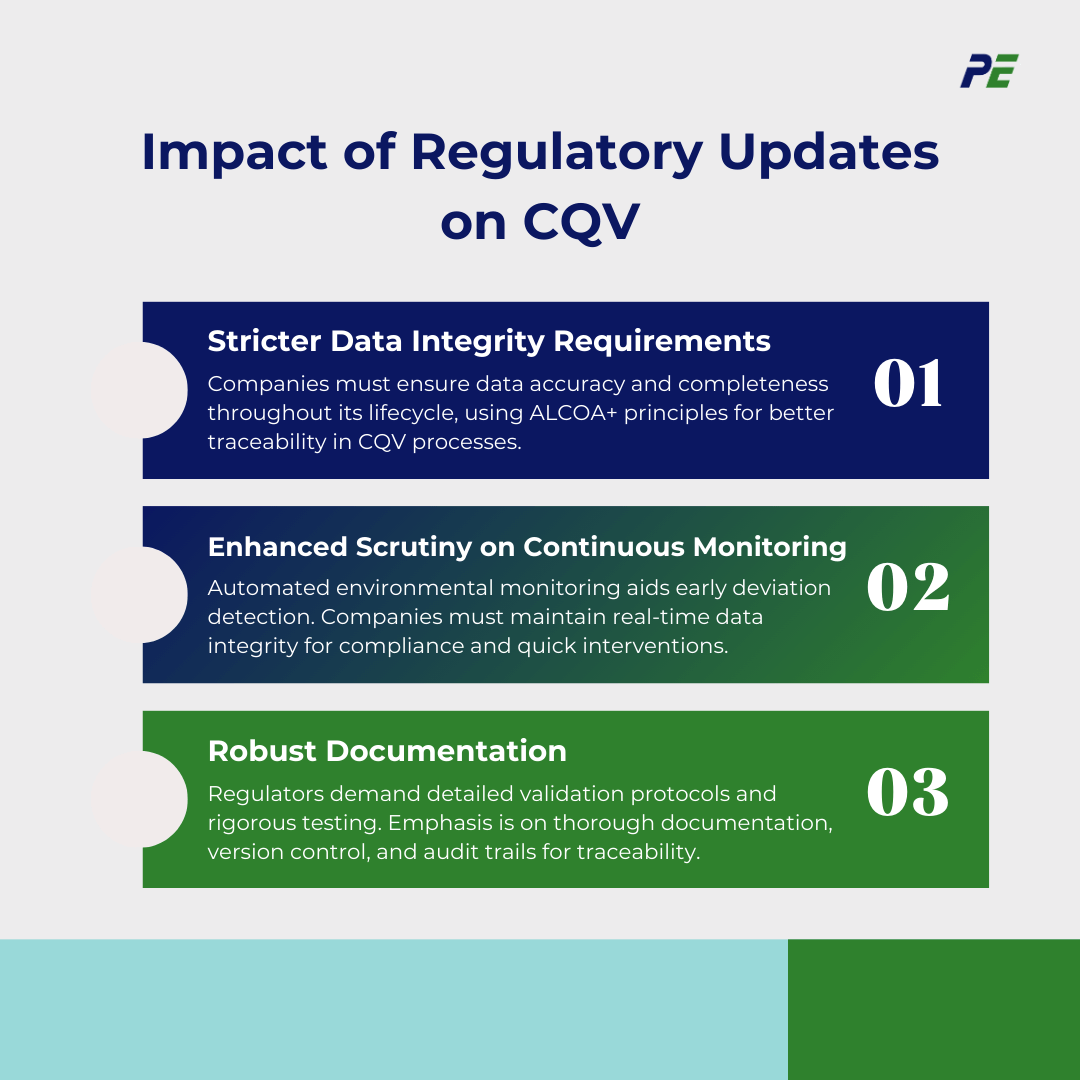
1. Stricter Data Integrity Requirements
Impact on CQV:
- Companies are now required to ensure that data is complete, consistent, and accurate throughout the entire data lifecycle (collection, processing, storage, and retrieval).
- The ALCOA+ principles are increasingly embedded into CQV processes to enhance data transparency and traceability.
2. Enhanced Scrutiny on Continuous Monitoring and Real-Time Data Collection
Impact on CQV:
- Automated monitoring of environmental factors (such as temperature, humidity, and pressure) and equipment performance ensures that deviations are detected earlier, minimizing product quality risks.
- Companies are required to implement robust systems that ensure real-time data integrity, enabling timely intervention and reducing the risk of regulatory non-compliance.
3. Robust Documentation
Impact on CQV:
- Regulatory bodies now require more detailed and robust validation protocols to demonstrate that systems are thoroughly tested and capable of maintaining product quality. This includes more rigorous testing of computerized systems.
- Increased focus on the completeness of validation documentation and the traceability of changes, including strict version control, change management, and audit trails.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the regulatory landscape for CQV continues to evolve due to advancements in technology, changing industry practices, and the increasing complexity of pharmaceutical processes. To remain compliant, companies must adapt to updated guidelines from global regulatory bodies like the FDA, EMA, and WHO. By adopting a risk-based approach, embracing new technologies, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, companies can ensure that their CQV processes not only meet regulatory demands but also enhance product quality and patient safety. Remaining proactive and informed about these changes will ensure long-term operational success in a highly regulated industry.
Partnering with PharmEng Technology
Partnering with PharmEng Technology is more than just a step toward compliance—it’s an investment in your company’s future success. Our deep expertise in Commissioning, Qualification, and Validation (CQV) ensures that your processes meet today’s stringent regulatory requirements and are adaptable to tomorrow’s evolving standards. From embracing cutting-edge technologies to maintaining strict quality control, we help you stay ahead in the competitive pharmaceutical landscape.
With a proven track record of delivering tailored solutions, we ensure your products are compliant, safe, and of the highest quality. Our team is dedicated to helping you streamline operations, reduce risk, and confidently navigate global regulations’ complexities.
Take the next step in securing compliance and operational efficiency. Reach out to us at info.asia@pharmeng.com to discover how PharmEng Technology can support your CQV needs and drive your business toward long-term success. Let’s shape the future of pharmaceutical excellence together!

About PharmEng Technology
PharmEng Technology is a global consulting firm specializing in pharmaceutical engineering, regulatory affairs, and compliance. With a commitment to quality and innovation, PharmEng Technology provides comprehensive solutions to meet the evolving needs of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries.
Contact Information
PharmEng Technology
Email: info.asia@pharmeng.com





