
Automation in CQV: Revolutionizing Pharmaceutical Processes
by Dhika Prameswari and Rida Hadirah Ramli
Automation in CQV is transforming the pharmaceutical industry by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and compliance. Traditional CQV methods, often manual and paper-based, can be labour-intensive, time-consuming, and prone to human error. However, the advent of digital tools and automated processes is revolutionizing how CQV is conducted, driving significant improvements in performance and innovation.
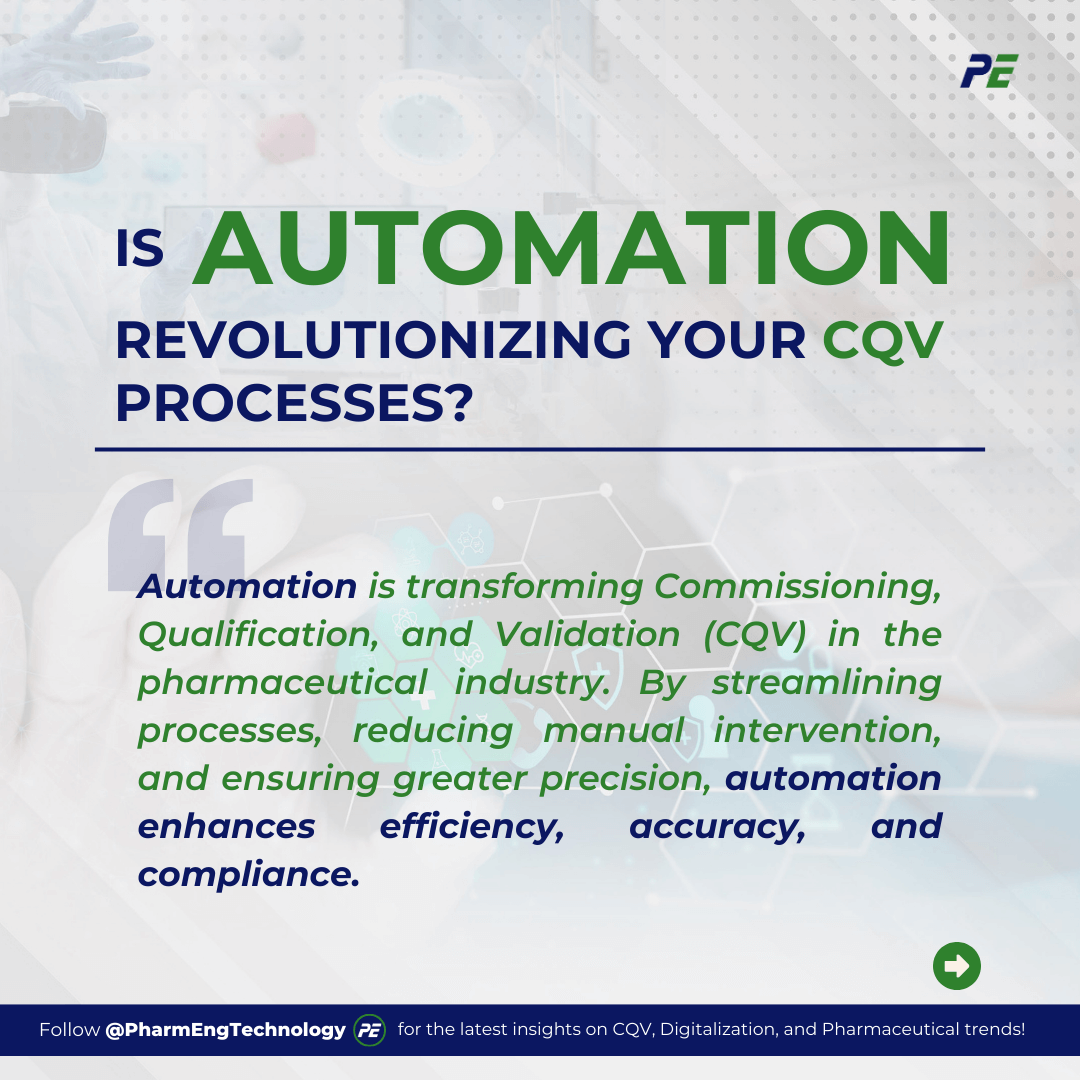
The Rise of Automation in Pharmaceuticals
In recent years, the pharmaceutical industry has undergone a significant transformation with the increasing adoption of automation and robotics. Driven by the need for enhanced efficiency, accuracy, and compliance with stringent regulatory requirements, these technologies are reshaping how pharmaceutical companies operate and deliver products. Below are the key drivers behind the growing adoption of automation and robotics:
- Efficiency Improvement
Automation streamlines production stages, from drug development to manufacturing and packaging, by handling repetitive tasks.
- Enhanced Accuracy
Automation in pharmaceutical manufacturing enhances accuracy by collecting precise data, and improving process monitoring, thereby ensuring product quality and safety.
- Regulatory Compliance
The pharmaceutical industry uses automation and robotics to ensure strict adherence to regulations, providing comprehensive documentation, traceability, and transparent audit trails during audits.
- Cost Reduction
Pharmaceutical companies can reduce labour costs and reallocate resources by automating repetitive tasks, minimizing material waste, and reworking.
- Scalability and Flexibility
Automation systems enable pharmaceutical companies to adapt to market fluctuations, improve process optimization, and decision-making through integration with AI and machine learning.
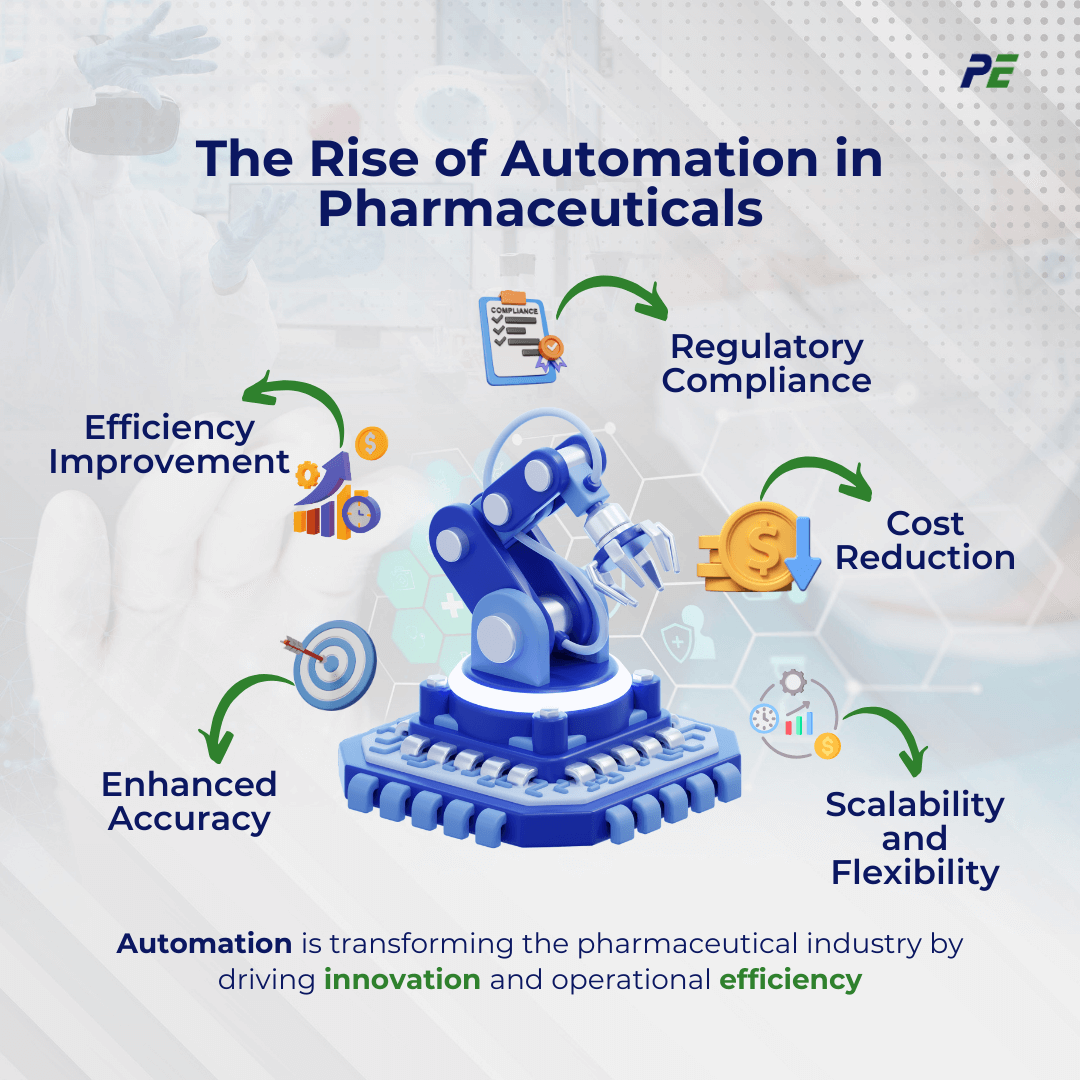
Automation in CQV: What It Means
Automation and robotics are revolutionizing the field of CQV in the pharmaceutical industry. These technologies play a crucial role in streamlining validation processes, reducing manual interventions, and enhancing the precision and consistency of validation activities. The following provides a detailed look at their roles and benefits:
- Streamlining Validation Process
- Automation tools collect data from validation stages, capturing real-time performance data, and accelerating both data collection and analysis. They ensure consistent and accurate recording, significantly reducing the likelihood of errors.
- Automation tools collect data from validation stages, capturing real-time performance data, and accelerating both data collection and analysis. They ensure consistent and accurate recording, significantly reducing the likelihood of errors.
- Reducing manual Interventions
- Automation reduces human error by handling routine tasks like calibration, testing, and data recording. Automation allows personnel to focus on strategic activities, enhancing efficiency and effectiveness in validation processes.
- Enhancing Precision and Consistency
- Robotics and automated systems offer high-precision measurement and control. Automation ensures consistent execution, reliable results, and reproducible outcomes for regulatory compliance and real-time product quality assurance.
Below are some of the examples of Automation and Robotics in CQV;
- Automated Testing Systems: These systems perform routine testing and data collection with minimal human intervention.
- Robotic Calibration: Automate the calibration of equipment and instruments, ensuring that they are set up correctly and consistently for each validation run.
- Automated Documentation: Simplifies the documentation process and ensures that all required information is accurately captured and maintained.
- Process Control Systems: Automated process control systems monitor and adjust manufacturing processes in real-time, ensuring that they remain within validated parameters throughout the production cycle.
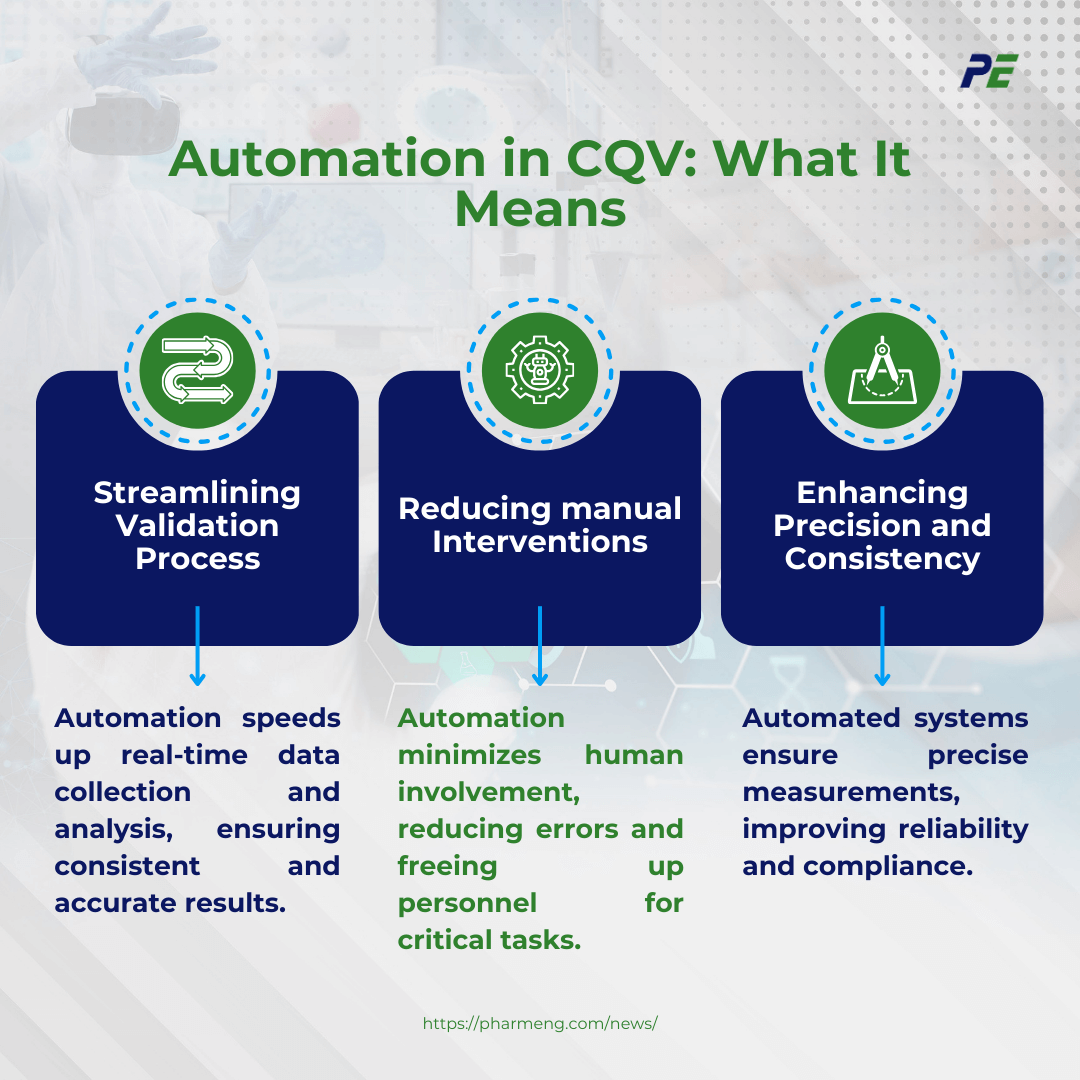
Key Technologies in Automated CQV
Automation in CQV is revolutionized by several key technologies, which enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and consistency of validation processes. Here is an exploration of the primary technologies driving this transformation:
- Robotics
- Robots are used for repetitive tasks like testing, sampling and measurement, equipment calibration, and maintenance. They reduce human error, ensure consistent protocol execution, and minimize manual handling risks.
- Automated Data Acquisition Systems
- Automated data acquisition systems collect real-time data from instruments and sensors, ensuring accurate analysis, reducing human error, and consistent recording across the validation process.
- AI/ML Algorithms for Process Monitoring
- AI and ML algorithms use historical data analysis to predict potential issues, improve process reliability, and identify anomalies. They continuously analyse data patterns, optimize processes, and reduce waste, resulting in improved performance and efficiency.
- Managing Validation Documentation
- Advanced software platforms streamline validation processes, from protocol creation to documentation, ensuring complete, accurate, and easily accessible documentation. They automate workflows, enhance team coordination, and execute activities according to predefined procedures.
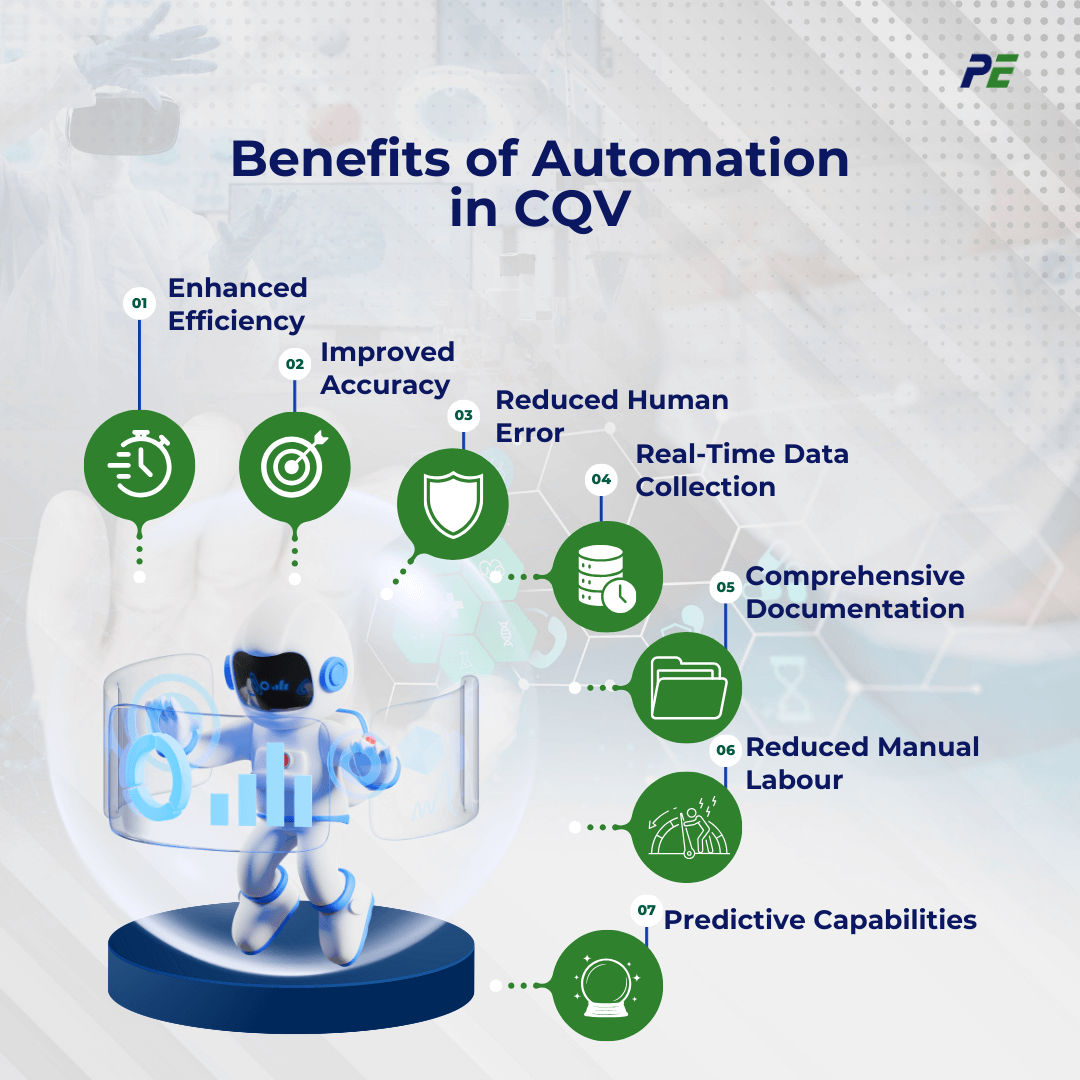
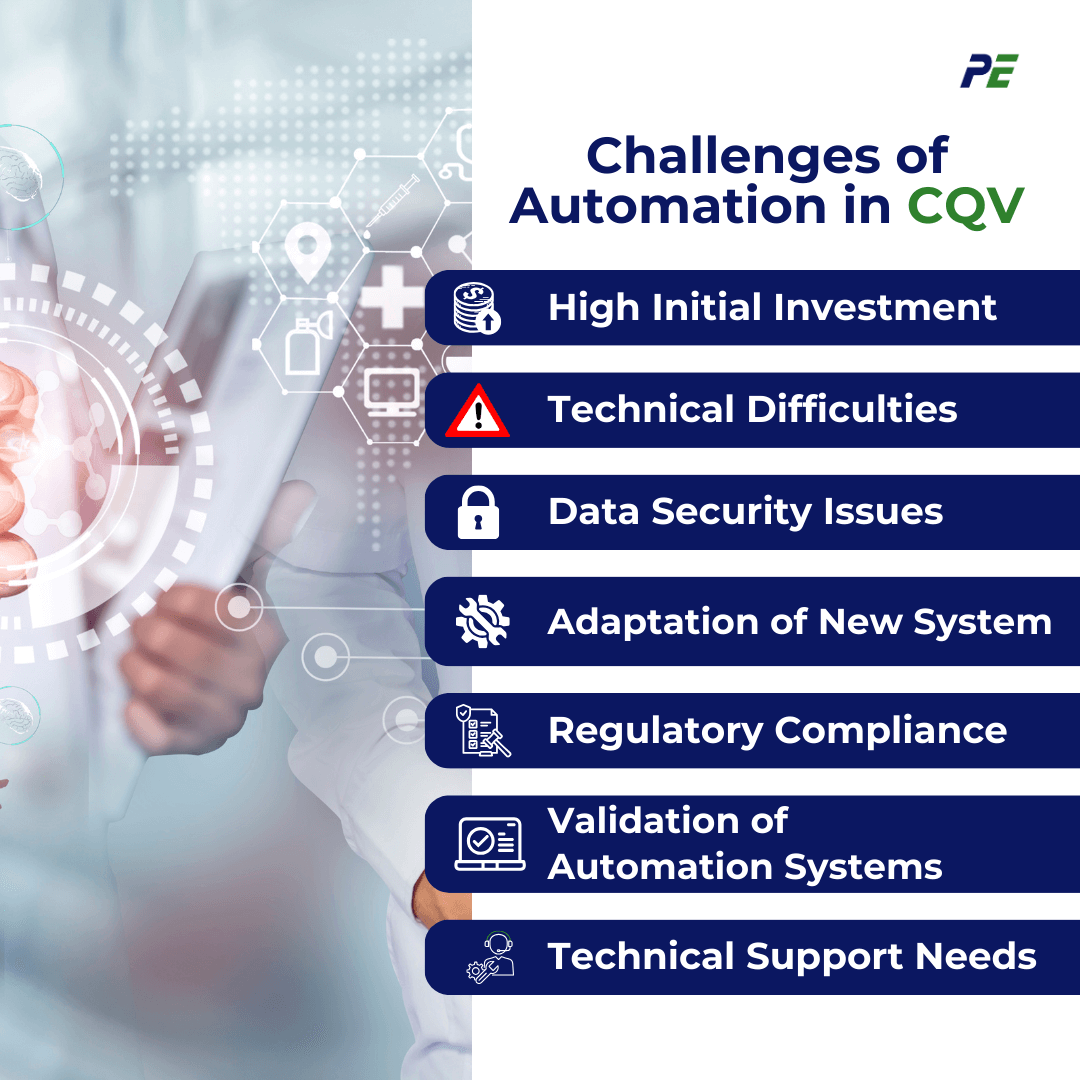
Benefits and Challenges
The shift toward automation in CQV brings significant opportunities but also introduces new complexities. As companies adopt these advanced technologies, they must navigate both the advantages and the potential hurdles that come with automation. Below are the benefits and challenges of implementing Automation in CQV:
Regulatory Perspective on Automation
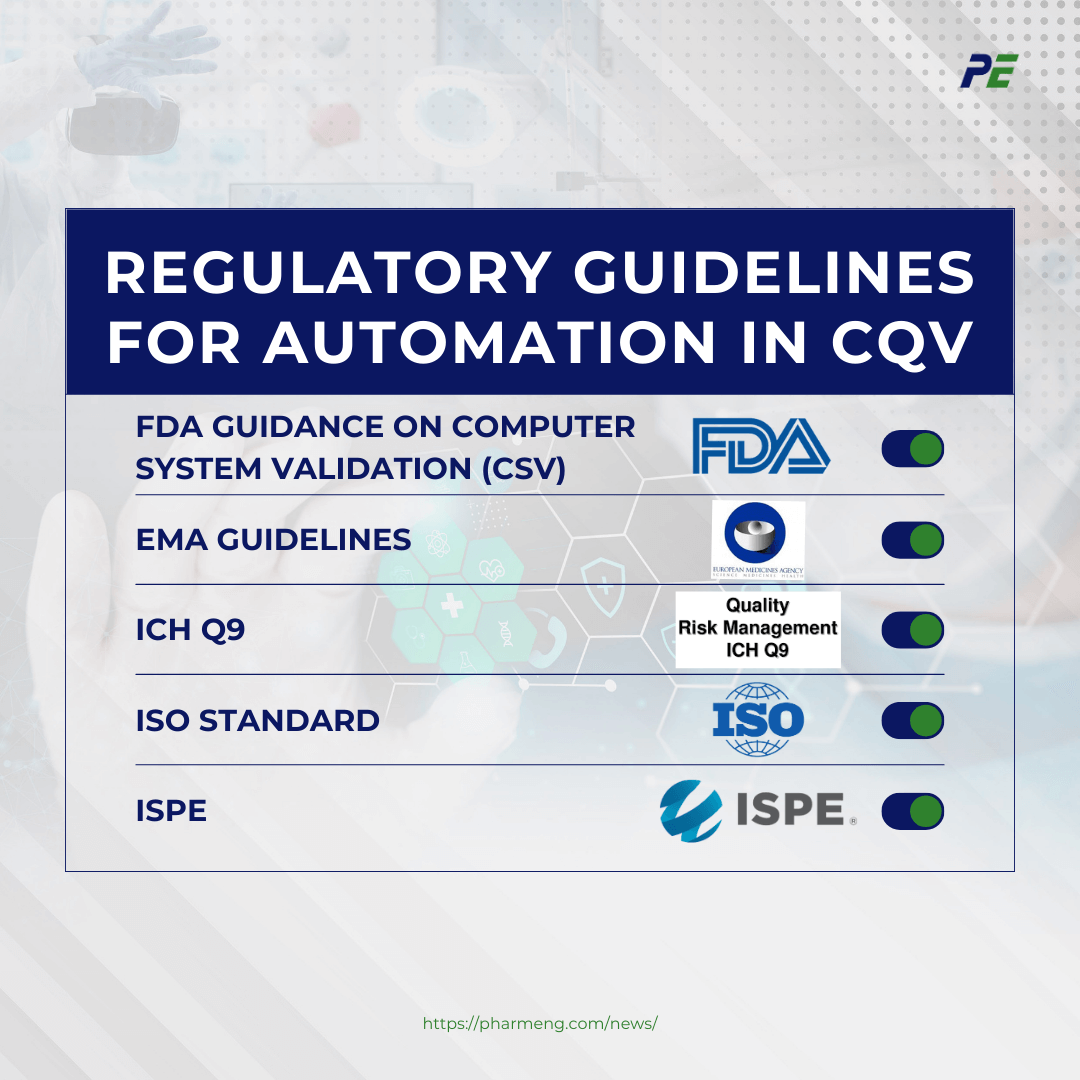
Regulatory bodies view automation in Commissioning, Qualification, and Validation (CQV) as a positive development, provided it adheres to guidelines and standards, enhancing efficiency and consistency. Here is a breakdown of the key documents and guidelines related to automated systems, focusing on FDA guidance, EMA guidelines, ICH Q9, ISO standards and ISPE:
- FDA Guidance on Computer System Validation (CSV): The FDA provides guidance on the validation of automated systems, ensuring that they meet the requirements for accuracy, reliability, consistent intended performance, and the ability to discern invalid or altered records. Key documents include:
- 21 CFR Part 11: Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures.
- General Principles of Software Validation; Final Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff.
- EMA Guidelines: The EMA emphasizes the need for validation and documentation of automated systems in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly concerning data integrity and GxP (Good Practice) requirements. Key documents include:
- EMA Guideline on GxP Data Integrity.
- EU GMP guide annexes: Annex 11: Computerized Systems
- ICH Q9: This document provides principles and examples of tools for quality risk management that can be applied to various aspects of pharmaceutical quality, including automated systems. Key points are:
- Promotes a risk-based approach to validation, where higher-risk systems receive more rigorous validation.
- Encourages the use of risk management tools like Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA) or Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) for assessing the impact of automated systems on product quality.
- Ensures that risk management is a continuous process, particularly important when implementing or changing automated systems.
- ISO Standard: Various ISO standards provide guidance on the quality and management of computerized systems in the pharmaceutical industry. One of the standards include:
- ISO 9001: Quality Management Systems
- ISO/IEC 27001: Information Security Management
- ISPE: GAMP (Good Automated Manufacturing Practice) guidelines, specifically address automated systems’ validation in the pharmaceutical industry.
- ISPE GAMP® 5 Guide: A Risk-Based Approach to Compliant GxP Computerized Systems
Conclusion
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to embrace automation and robotics, the impact on CQV processes is undeniable. Implementing automation in CQV offers significant benefits in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and consistency. However, it also presents challenges such as high initial investment, complexity in integration, and regulatory compliance requirements. Despite these hurdles, the future of CQV is set to be increasingly automated, with the potential to not only revolutionise pharmaceutical manufacturing but also to set new standards for quality and safety in the industry.
Partnering with PharmEng Technology
Partnering with PharmEng Technology provides you with a trusted pathway to achieving pharmaceutical compliance, operational efficiency, and innovation. We specialize in optimizing processes, ensuring that your organization meets industry standards while driving continuous improvement and innovation. With a deep understanding of the pharmaceutical industry and a focus on tailored solutions, PharmEng Technology helps you not only meet but exceed your validation and compliance objectives.
For more information on how PharmEng Technology can support your pharmaceutical compliance and operational goals, we invite you to discuss how we can help your organization achieve its validation objectives, please reach out to us at info.asia@pharmeng.com. Let us partner with you in driving innovation and operational excellence in the pharmaceutical sector.

About PharmEng Technology
PharmEng Technology is a global consulting firm specializing in pharmaceutical engineering, regulatory affairs, and compliance. With a commitment to quality and innovation, PharmEng Technology provides comprehensive solutions to meet the evolving needs of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries.
Contact Information
PharmEng Technology
Email: info.asia@pharmeng.com





