
Risk-Based CQV: Enhancing Efficiency and Compliance Part 2
by Dhika Prameswari and Rida Hadirah Ramli
In the previous article, we discussed the principles of risk management, the challenges inherent in traditional CQV, and the significant benefits that a risk-based approach brings to Commissioning, Qualification, and Validation (CQV) processes. Building on that foundation, this section will delve into practical steps for implementing a risk-based CQV framework and the regulatory guidelines that support it.
Implementing Risk-Based CQV
Quality Risk Management (QRM) is a structured process that involves assessing, controlling, communicating, and reviewing risks to ensure the quality of drug products throughout their lifecycle. The process, typically represented in a model such as the one outlined in Figure 1, can vary in emphasis depending on the specific context, but a comprehensive approach will always consider each component of the framework. The depth of detail for each element should align with the level of risk associated with the process or product in question, ensuring that risks are managed appropriately to maintain product quality.
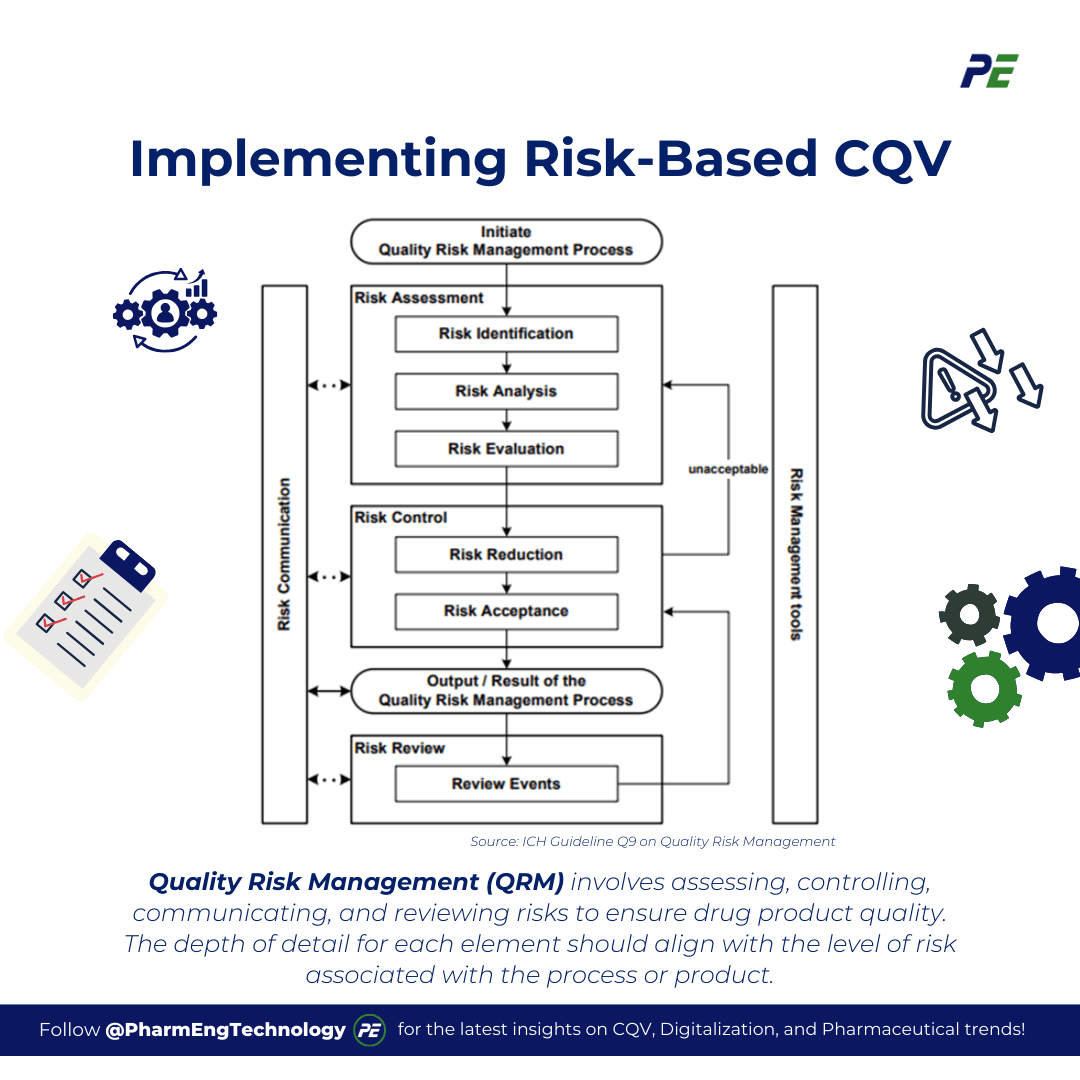
Source: ICH Guideline Q9 on Quality Risk Management
This summary guide provides encouragement and actionable steps for organizations aiming to initiate or enhance their Quality Risk Management (QRM) practices within the context of Commissioning, Qualification, and Validation (CQV). Below are the key steps involved in ensuring a robust and effective QRM process:
- Risk Assessment is one of a crucial part of the QRM process and involves the following components
- Risk Identification is the systematic process of identifying potential hazards and risks associated with a given problem or risk question. The objective is to identify possible hazards and the consequences of these hazards. This forms the foundation for the entire risk management process.
- Risk Analysis, this step involves estimating the risk associated with the identified hazards. It is a qualitative or quantitative process that connects the likelihood of occurrence with the severity of potential harm. The goal is to understand the nature of the risks, their causes, and their potential impact on the product’s quality and safety.
- Risk Evaluation, in this step, the identified and analysed risks are compared against predefined risk criteria to assess their significance. The aim is to determine which risks are acceptable and which require further control or mitigation measures.
- Risk control is aimed at reducing and/or accepting risks to ensure that they remain within an acceptable level. Here is a detailed look at the key elements of risk control:
- Risk reduction involves identifying and implementing processes to mitigate or avoid risks that exceed the acceptable level. This can include measures to reduce the severity and probability of harm. Additionally, enhancing the detectability of potential hazards and risks is a key strategy in reducing overall risk.
- Risk acceptance, this can be a formal decision where the residual risk is explicitly acknowledged, or it can be a passive decision where the residual risks are not clearly defined.
- Risk communication is vital in Quality Risk Management (QRM) as it facilitates information exchange among stakeholders about identified risks, management decisions, and risk control strategies. Proper communication and documentation of QRM results ensure all parties have access to the same information, facilitating coordinated risk management efforts.
- Risk review should be an ongoing part of quality management, continuously monitored and reviewed to adapt to new information and changing conditions. A structured mechanism should be in place to regularly evaluate risk outcomes and respond to events. Integrating new knowledge and experience into the risk management process ensures decisions remain relevant and effective. The frequency of risk reviews should be proportional to the level of risk involved.
By following these steps, pharmaceutical companies can ensure that their CQV processes are robust, efficient, and aligned with regulatory expectations, ultimately safeguarding product quality and patient safety.

Regulatory Guidance on Risk-Based CQV
After detailing the principles and implementation of risk-based CQV, the following regulatory guidance is provided to support this approach:
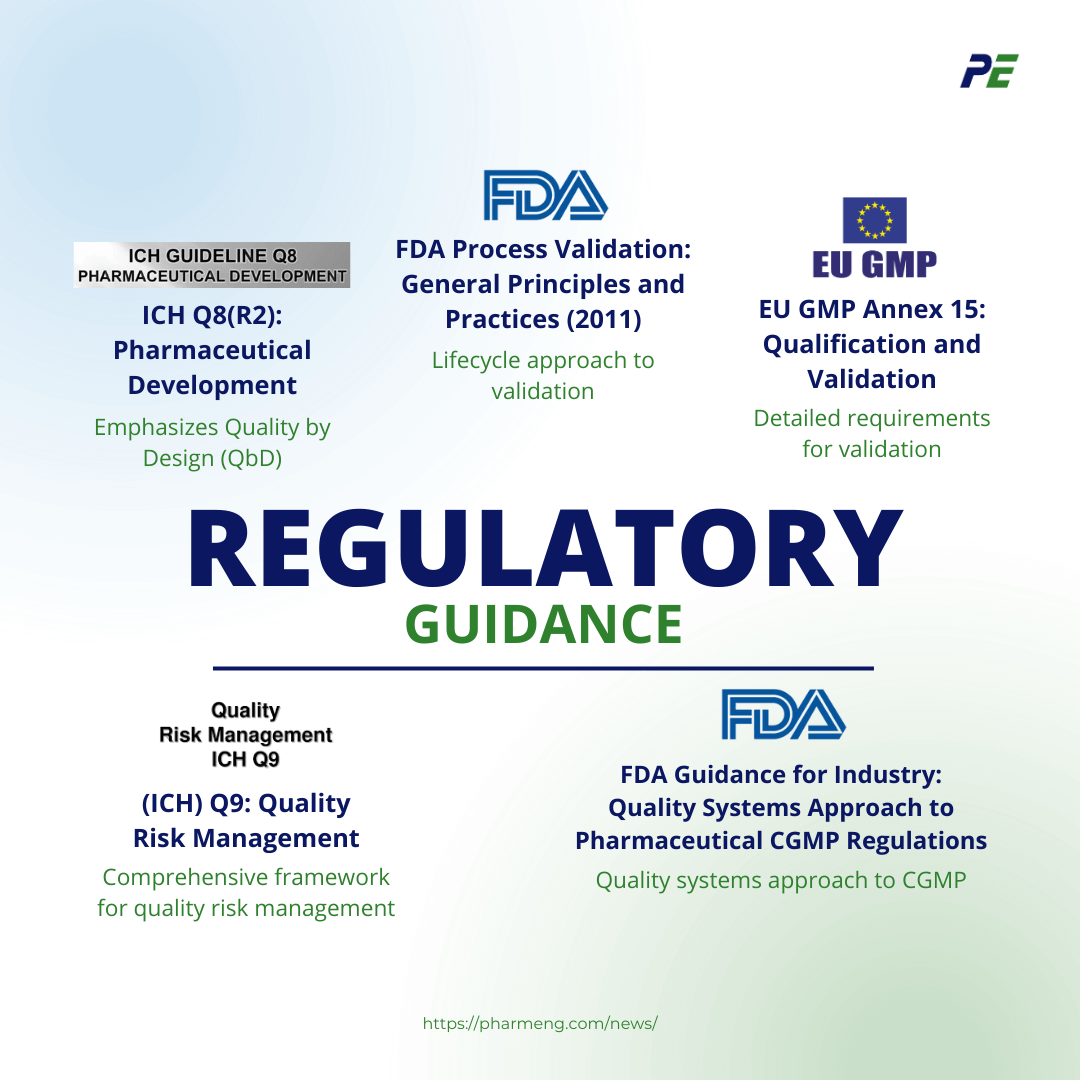
- (ICH) Q9: Quality Risk Management
- Overview: ICH Q9 provides a comprehensive framework for quality risk management, which is integral to a risk-based CQV approach. It outlines the principles and tools for assessing, controlling, communicating, and reviewing risks throughout the product lifecycle.
- Relevance to CQV: This guideline encourages the application of risk management to all aspects of CQV, ensuring that resources are focused on the most critical areas that could impact product quality and patient safety.
- ICH Q8(R2): Pharmaceutical Development
- Overview: ICH Q8(R2) emphasizes the importance of understanding the relationship between process variables and product quality. It introduces the concept of Quality by Design (QbD), where risk-based approaches are used to design processes that are robust and capable of consistently delivering quality products.
- Relevance to CQV: In the context of CQV, ICH Q8(R2) supports the identification and control of critical process parameters (CPPs) and critical quality attributes (CQAs), guiding the validation efforts towards areas of highest risk.
- FDA Process Validation: General Principles and Practices (2011)
- Overview: This guidance document outlines the FDA’s expectations for process validation, emphasizing a lifecycle approach that includes process design, process qualification, and continued process verification.
- Relevance to CQV: It supports the integration of risk-based principles throughout the CQV process, particularly in the continuous monitoring and control of validated processes to ensure ongoing compliance and product quality.
- EU GMP Annex 15: Qualification and Validation
- Overview: Annex 15 of the EU GMP guidelines provides detailed requirements for the qualification and validation of equipment, facilities, utilities, and processes. It advocates for the use of a risk-based approach to focus efforts on critical aspects of the manufacturing process.
- Relevance to CQV: This annex is crucial for implementing a risk-based CQV strategy in Europe, ensuring that validation efforts are aligned with regulatory expectations while optimizing resource allocation.
- FDA Guidance for Industry: Quality Systems Approach to Pharmaceutical CGMP Regulations
- Overview: This guidance highlights the importance of implementing a quality systems approach to Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) regulations. It emphasizes the role of risk management in ensuring consistent product quality.
- Relevance to CQV: By adopting a quality systems approach, organizations can integrate risk-based CQV within their overall quality management system, ensuring a holistic approach to compliance and product quality.
These regulatory guidelines and industry standards provide a robust foundation for implementing risk-based CQV, ensuring that validation efforts are both efficient and compliant with global regulatory requirements. By following these guidelines, organizations can optimize their CQV processes, focus on critical areas, and maintain high standards of quality and compliance.
Conclusion
Implementing Quality Risk Management (QRM) in Commissioning, Qualification, and Validation projects is not just a regulatory requirement; it is a strategic imperative for ensuring the success of commissioning, qualification, and validation projects. By embracing these steps, organizations can create a culture of excellence, collaboration, and adaptability, ultimately enhancing the overall quality and compliance of their CQV projects.
Why PharmEng Technology?
PharmEng Technology delivers innovative solutions to tackle inefficiencies in traditional commissioning and qualification processes. Our advanced platform replaces cumbersome paper-based documentation with streamlined digital workflows, enhancing accuracy and operational efficiency. With support for electronic execution, we minimize the time and effort required for validation activities, ensuring adherence to regulatory standards.
Our centralized repository simplifies information access, sharing, and tracking throughout the project lifecycle, fostering greater productivity and transparency. This holistic approach not only boosts reliability and security but also optimizes the entire commissioning and qualification process.
Explore how PharmEng Technology can revolutionize your operations by visiting www.pharmeng.com or reaching out to us at info.asia@pharmeng.com. Let’s drive your success together!

About PharmEng Technology
PharmEng Technology is a global consulting firm specializing in pharmaceutical engineering, regulatory affairs, and compliance. With a commitment to quality and innovation, PharmEng Technology provides comprehensive solutions to meet the evolving needs of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries.
Contact Information
PharmEng Technology
Email: info.asia@pharmeng.com





